In recent years, our understanding of gut health has undergone a significant transformation. We've moved beyond the well-known probiotics to discover two emerging categories that play a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy gut: prebiotics and postbiotics. These lesser-known components are gaining recognition for their profound impact on gut health and immune function. In this blog post, we will delve into why gut health is important, what prebiotics and postbiotics are, how they compare to probiotics, and why they are essential for overall well-being.
Why is Gut Health Important?
Gut health is a linchpin for overall well-being. The gut, often referred to as the "second brain," is a complex ecosystem where trillions of microorganisms reside. This microbiome plays a critical role in not only digestion and nutrient absorption but also in influencing the immune system. The gut and the immune system are intricately connected, with approximately 70% of the body's immune cells residing in the gut.
A healthy gut microbiome helps to maintain a balanced immune response, distinguishing between harmful pathogens and beneficial microorganisms. When the gut is in good condition, it can effectively protect the body from infections, regulate inflammation, and contribute to better immune function. Hence, nurturing gut health is a fundamental step in promoting overall health and resilience against various diseases.
What are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are a type of dietary fiber that serve as fuel for the beneficial microorganisms living in our gut, primarily bacteria. These indigestible compounds are found in various plant-based foods such as onions, garlic, bananas, asparagus, and chicory root. Prebiotics act as sustenance for probiotics, helping them thrive and multiply.
How Prebiotics Differ from Probiotics
While probiotics are live microorganisms, such as beneficial bacteria and yeast, prebiotics are non-living, plant-derived compounds. Probiotics are found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, as well as in dietary supplements. In contrast, prebiotics are present in many everyday foods, making it easier to incorporate them into your diet.
Benefits of Prebiotics
Prebiotics and probiotics go hand-in-hand, working together to support gut health. Prebiotics provide the nourishment necessary for the growth and activity of probiotics. This partnership fosters a balanced and diverse gut microbiome, which is essential for a healthy digestive system and a robust immune response.
Here are some of the direct benefits of prebiotics:
- Help regulate bowel movements.
- Produce neurotransmitters that go back and forth between your gut and your brain to trigger mood changes and other processes.
- Stimulate your body to make hormones that aid in appetite, appetite suppression and more.
- Help your bones mineralize and absorb calcium and phosphorus, which can improve bone density.
- Improve how well your immune system functions.
- Enhance your body’s anti-inflammatory response.
- Increase production of good bacteria and decrease bad bacteria that causes disease.
What are Postbiotics?
Postbiotics are a newer addition to the field of gut health, and they offer an intriguing perspective on maintaining a well-balanced gut microbiome. Postbiotics are the metabolic byproducts produced when probiotics consume prebiotics. These byproducts include short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), vitamins, enzymes, and other bioactive compounds. Unlike probiotics and prebiotics, postbiotics do not require live microorganisms. Instead, they harness the power of the substances produced during the fermentation process.
Benefits of Postbiotics
Postbiotics play a significant role in promoting gut health and overall well-being:
1. Gut Barrier Integrity: Postbiotics help maintain the integrity of the gut lining, preventing the entry of harmful substances into the bloodstream and reducing inflammation.
2. Immune Function: The gut is closely linked to the immune system, and postbiotics can modulate immune responses. SCFAs, for example, have anti-inflammatory properties that support the immune system's proper function.
3. Metabolic Health: Postbiotics, especially SCFAs, have been associated with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced risk of obesity and related conditions.
4. Neurological Health: Recent research suggests that postbiotics may influence the gut-brain axis, potentially benefiting mental health and cognitive function.
Conclusion
While probiotics have long been celebrated for their role in gut health, the emergence of prebiotics and postbiotics has expanded our understanding of the complex ecosystem residing in our digestive system. Prebiotics provide the essential nutrients for probiotics to thrive, while postbiotics offer numerous health benefits derived from the metabolic activity of these beneficial microorganisms.
The future of gut health is an exciting one, with prebiotics and postbiotics at the forefront of scientific research and wellness trends.

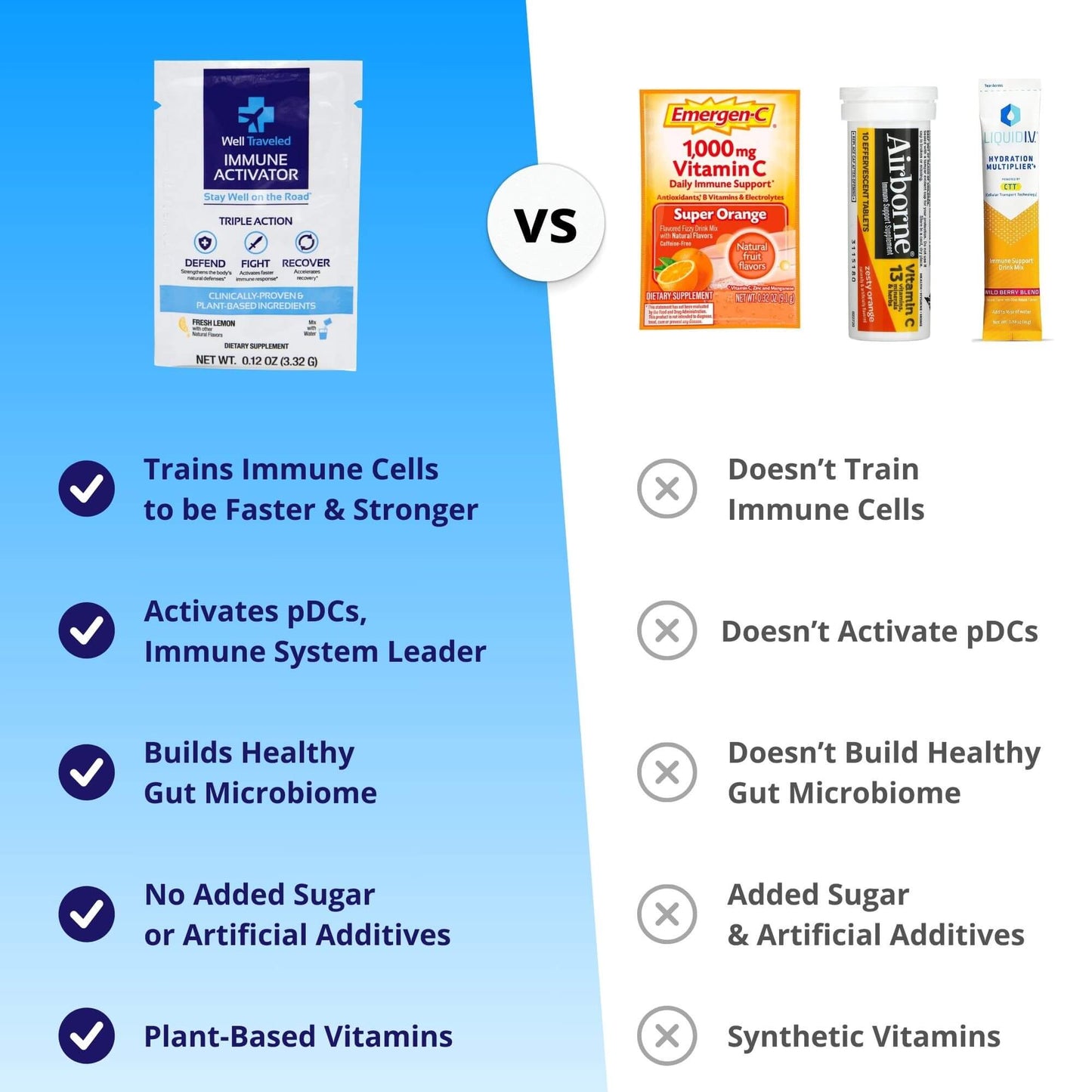
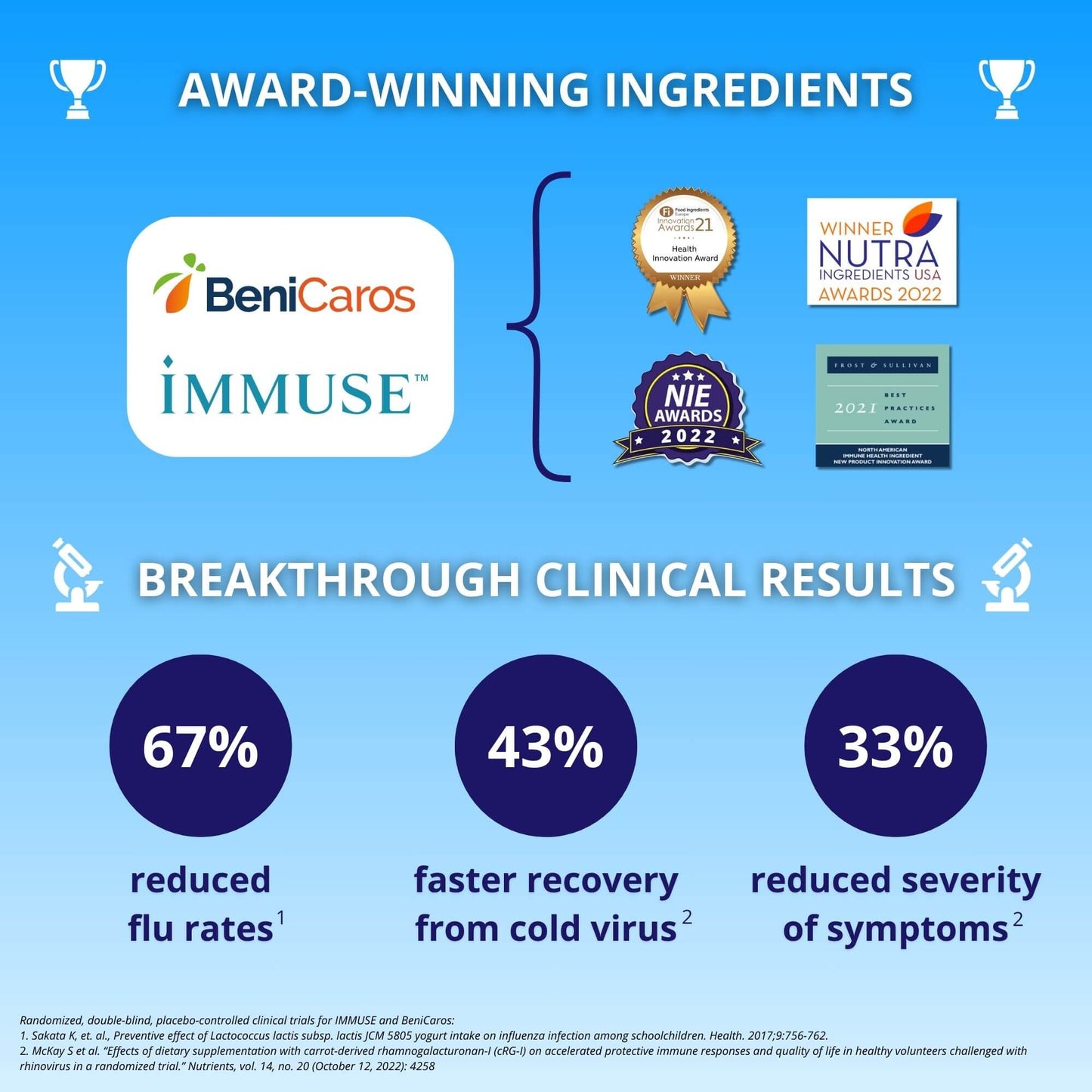
By incorporating prebiotics and postbiotics into your diet with a supplement like Well Traveled, you can enhance your gut health, boost your immune function, and improve your overall well-being.
Sources:
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/what-are-prebiotics